From the barricades of the Paris Commune to anti-colonial resistance in the South Pacific, Louise Michel was one of the most important revolutionaries of the 19th century.
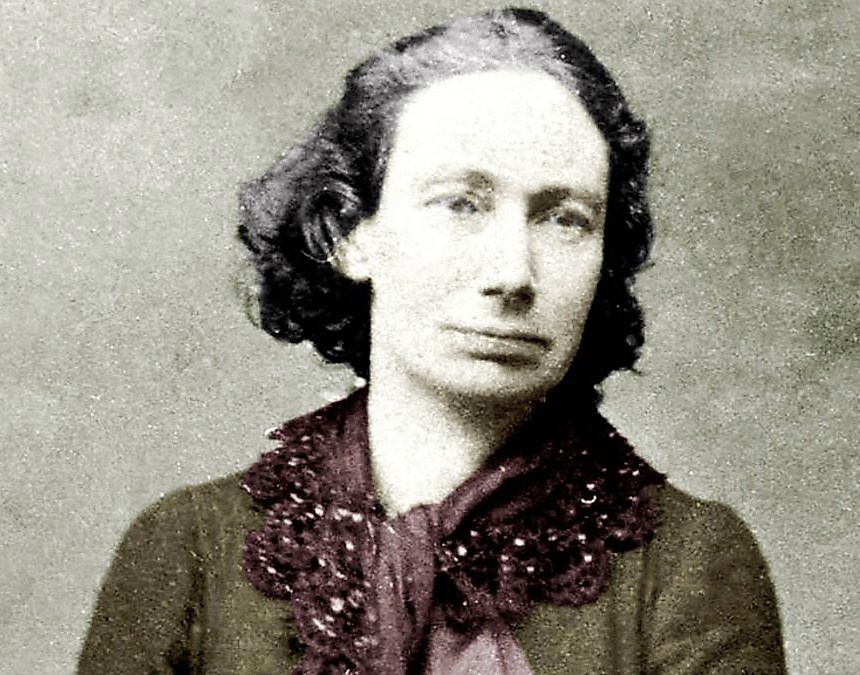
Louise Michel, born on 29 May, 1830, is today remembered as one of the most influential and charismatic revolutionaries of the 19th century. Her role in the Paris Commune of 1871 — first in the ambulance service and later on the front lines with the National Guard fighting against the Versailles troops — eventually led to her capture and deportation from France to a penal colony in New Caledonia.
It was during her exile that Michel turned towards anarchism, which would continue to dominate her writing and organizing for the rest of her life. In 1880 she was granted amnesty, and upon her return to France she continued her revolutionary activities, writing articles, giving speeches, setting up a soup kitchen for impoverished ex-prisoners who returned from exile, and traveling across Europe delivering her revolutionary message to large audiences. In 1890 she opened the International Anarchist School for children on London’s Fitzroy Square, before returning to France in 1895. Michel died on 10 January, 1905, after which her funeral in Paris was attended by more than 100,000 people.